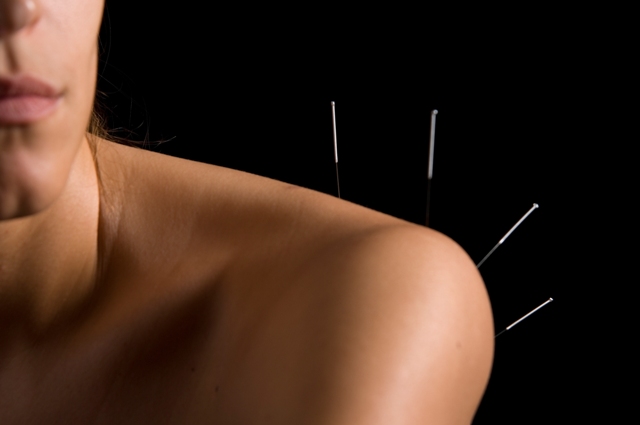
Court Dismisses Lawsuit Filed by NC Acupuncture Licensing Board
Advocates for North Carolina physical therapists (PTs) have scored a victory by way of a superior court, which dismissed a lawsuit brought by the North Carolina Acupuncture Licensing Board (NCALB) against the North Carolina Board of Physical Therapy Examiners (NCBPTE), several PTs, and a physical therapy practice over the issue of dry needling by PTs. […]
Court Dismisses Lawsuit Filed by NC Acupuncture Licensing Board Read More »